The Daily Insight
Stay updated with the latest news and insights.
Bulking Up the Right Way: Feed Your Gains
Unlock the secrets to effective bulking! Discover expert tips to optimize your diet and fuel your gains like never before.
The Ultimate Guide to Nutrition for Bulking: What to Eat and When
When it comes to nutrition for bulking, understanding what to eat and when to eat it is crucial for maximizing muscle gains. Bulking requires a calorie surplus, meaning you need to consume more calories than you expend. Focus on nutrient-dense foods such as lean proteins, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats. Protein sources like chicken, turkey, fish, and legumes are essential for muscle repair and growth. Incorporate complex carbs such as quinoa, brown rice, and oats into your meals to fuel your workouts and replenish glycogen stores.
Timing your meals is equally important in a bulking regimen. Aim for 5-6 meals per day, spaced 2-3 hours apart, to provide a steady stream of nutrients for muscle recovery. Consider an anabolic window strategy by consuming a meal or snack rich in protein and carbs within 30 minutes post-workout to jumpstart recovery. Additionally, healthy fats from avocados, nuts, and olive oil will provide essential fatty acids and aid in hormone production, which is vital for muscle growth. Remember, consistency in both nutrition for bulking and training will yield the best results.
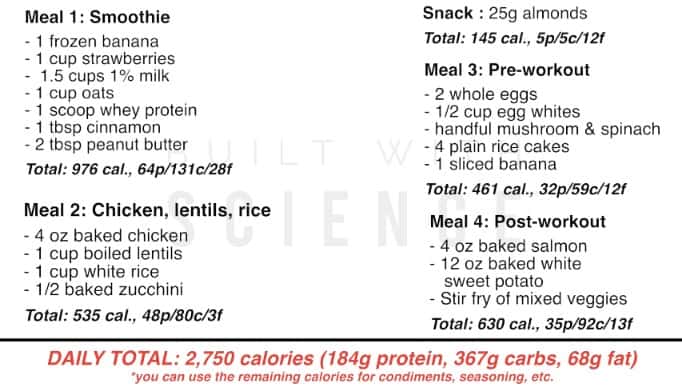
Common Bulking Mistakes: How to Avoid Gaining Unwanted Fat
One of the most prevalent bulking mistakes that many new bodybuilders make is underestimating the importance of proper macronutrient ratios. Focusing solely on increasing calorie intake without considering the balance of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates can lead to the accumulation of unwanted fat instead of lean muscle. To avoid gaining unwanted fat, it is essential to calculate your daily caloric needs accurately and adjust your macronutrient intake accordingly. Aim for a diet that includes plenty of high-quality protein sources, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats to fuel your workouts and recovery effectively.
Another critical error is neglecting cardiovascular exercise during a bulking phase. While the primary focus should be on strength training and muscle gain, incorporating cardio a few times a week can help maintain a healthy metabolism and prevent excess fat gain. Consider adding high-intensity interval training (HIIT) or moderate-intensity steady-state cardio sessions to your routine. To summarize, avoid the common pitfalls of improper macronutrient management and lack of cardiovascular activity to ensure that your bulking phase is anabolic, not a recipe for unwanted fat gain.
How to Calculate Your Caloric Needs for Optimal Muscle Growth
To effectively calculate your caloric needs for optimal muscle growth, start by determining your Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE). This involves calculating your Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR), which is the number of calories your body needs at rest. You can estimate your BMR using the Mifflin-St Jeor equation: BMR = 10 × weight (kg) + 6.25 × height (cm) - 5 × age (years) + 5 (for men) or -161 (for women). Once you have your BMR, multiply it by an activity factor that matches your lifestyle (e.g., sedentary, moderately active, or highly active) to find your TDEE.
After establishing your TDEE, it's time to create a caloric surplus to facilitate muscle growth. A good starting point is to add 250 to 500 calories to your TDEE, depending on your individual goals and how aggressive you want your muscle gain to be. It's important to monitor your progress and adjust caloric intake accordingly to ensure you're gaining muscle without excess fat. Remember, consistency in both nutrition and training is key for maximum results.